In this article we will learn about arrays, first, we learn some fundamental concepts of arrays and then move to some essential array methods.
let's get start
what is an array?
An array is generally described as "list-like objects", they are basically single objects that contain multiple values stored in a list. Array objects can be stored in variables.
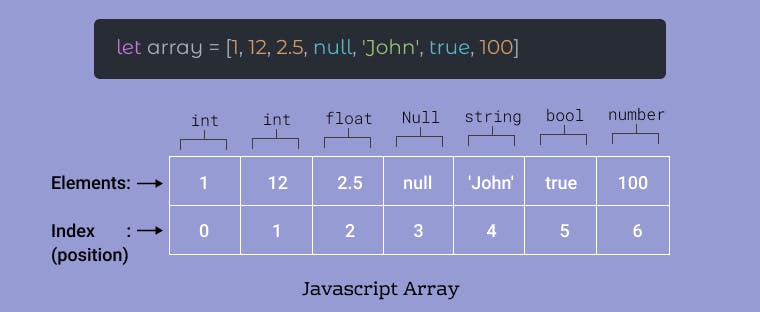
An array can hold values of mixed types. For example, you can have an array that stores elements with the types number, string, and boolean.
The size of an array is dynamic and auto-growing. In other words, you don’t need to specify the array size up front. we can access each value inside the arrays individually, To access an element in an array, you specify an index in the square brackets [ ]: arrayName[index]
const names = ["pranit", "ingole", " mayur", "yachi" , 1, true];
console.log(names[0]) // pranit
console.log(names[2]) // mayur
console.log(names[3]) // yachi
console.log(names[4]) //1
console.log(names[5]) //true
Efficient things with the array, like loop through it and do the same thing to every value. Maybe we've got a series of product items and their prices stored in an array, and we want to loop through them all and print them out on an invoice while totaling all the prices together and printing out the total price at the bottom.
If we didn't have arrays, we'd have to store every item in a separate variable, then call the code that does the printing and adding separately for each item. This would be much longer to write out, less efficient, and more error-prone. If we had 10 items to add to the invoice it would already be annoying, but what about 100 items, or 1000? ya, that's why we have an array.
you should know before the move
About let const var with primitive and non-primitive data type
Create an Array
There are two ways to create a arrays
first way
const names = ["pranit", "ingole", " mayur", "yachi" , 1, true];
// with const we need to declare and initialization simultaneously at first
// we can't reassign it with another variable
another one
You can also create an array using JavaScript's new keyword.
const myarray = new Array(1, 2, 3);
Note creating an array with new keywords not recommended
Now time start learning about the array of methods
- length property
you can find out the length of the array with the length property
const mycollegeFriends = ["Harsh", "Mayur", "Abhay"];
console.log(mycollegeFriends.length) //3
console.log(mycollegeFriends[mycollegeFriends.length - 1])
//last element// Abhay
Note in javascript primitive value immutable, only reference types are mutable for eg Array in js that's why we are able to change the array element by indexing just one condition, we can't reassign. array with const variable.
- push() Method
push method we used to push the element or elements in the array
const mycollegeFriends = ["Harsh", "Mayur", "Abhay", "yachi"];
mycollegeFriends.push("Aryan", "Nikhil");
console.log(mycollegeFriends);
output -> ['Harsh', 'Mayur', 'Abhay', 'yachi', 'Aryan', 'Nikhil']
// push method also return current length of array
const newfriendlistlength = mycollegeFriends.push("Aryan", "Nikhil");
console.log(newfriendlistlength) // 6
unshift() Method
The unshift() method adds one or more elements to the beginning of an array and returns the new length of the array.
const mycollegeFriends = ['Harsh', 'Mayur', 'Abhay', 'yachi', 'Aryan', 'Nikhil'];
const some = mycollegeFriends.unshift("Bhushan");
console.log(mycollegeFriends)
// ['Bhushan', 'Harsh', 'Mayur', 'Abhay', 'yachi', 'Aryan', 'Nikhil', 'Aryan', 'Nikhil'];
console.log(some)// 9 // just like push , unshift also return length of array
- pop() method
The pop() method removes the last element from an array and returns that element. This method changes the length of the array.
const mycollegeFriends = ['Bhushan', 'Harsh', 'Mayur', 'Abhay', 'yachi', 'Aryan', 'Nikhil'];
const popped = mycollegeFriends.pop();
console.log(mycollegeFriends);// ['Bhushan', 'Harsh', 'Mayur', 'Abhay', 'yachi', 'Aryan']
console.log(popped);// Nikhil // It will return pop element
- shift() method
The shift() method removes the first element from an array and returns that removed element. This method changes the length of the array.
const mycollegeFriends = ['Bhushan', 'Harsh', 'Mayur', 'Abhay', 'yachi', 'Aryan', 'Nikhil'];
const fromfront = mycollegeFriends.shift();
console.log(mycollegeFriends);// ['Harsh', 'Mayur', 'Abhay', 'yachi', 'Aryan']
console.log(fromfront);// Bhushan // It will return element from front
- indexof() method
The indexOf() method returns the first index at which a given element can be found in the array, or -1 if it is not present.
const mycollegeFriends = ['Bhushan', 'Harsh', 'Mayur', 'Abhay', 'yachi', 'Aryan', 'Nikhil'];
console.log(mycollegeFriends.indexOf("yachi"));// 4 // it will return index number of element
// what about those element not present and you try to used indexOf() method to find index number..........
console.log(mycollegeFriends.indexOf("Anurag"));// -1// because i try find index which not present in array
- includes() method
The includes() method determines whether an array includes a certain value among its entries, returning true or false as appropriate.
const mycollegeFriends = ['Bhushan', 'Harsh', 'Mayur', 'Abhay', 'yachi', 'Aryan', 'Nikhil'];
mycollegeFriends.push(17);
console.log(mycollegeFriends.includes("Mayur")); //true
console.log(mycollegeFriends.includes("Bhushan")); //true
console.log(mycollegeFriends.includes("bhushan")); //flase // beacuse not same elemnt
console.log(mycollegeFriends.includes("44")); //false
console.log(mycollegeFriends.includes("17")); //flase
console.log(mycollegeFriends.includes(17)); // true
if (mycollegeFriends.includes("Mayur")) {
console.log("you have call from mayur");
};
// you have call from mayur